Sara Stamas made this product. GitKraken is a Git GUI client for not only Mac, but also Windows and Linux. It's a visual UI for Git that’s not only beautiful, but is also a true time-saver for Git beginners and pros. GitKraken simplifies complicated commands into drag and drop actions.
- 10 Best GUI Git Clients for Mac 1. Fork is a free advanced GUI git client for Mac and Windows with an emphasis on speed, user-friendliness,. GitHub Desktop is a completely free and open source customizable Electron-based Git client app. Sourcetree is a.
- Git config -global user.name 'Firstname Lastname' git config -global user.email 'youremail@youremail.com' In case you are using Beanstalk for version control, it would be best if your first name, last name and email address match to the ones you use in your account to avoid any conflicts.
ROMS source code is distributed using both Git and Subversion(SVN). The Git repository includes the full history of changes to the ROMS source code. Details on using Subversion can be found here. There are command line and GUI Git clients available for nearly every operating system and a list of popular clients can be found here. This page will help you get started with downloading ROMS with Git.
- 2Saving ROMS Login Credentials
- 3Downloading ROMS
- 4Using GUI Git Clients
- 5Managing Your Own Modifications
Git Overview
Git is a free and open source distributed version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency. All the ROMS/TOMS files are stored in a Git repository on www.myroms.org with access controlled by requiring authentication with the same ROMS Username/Password combination assigned to registered users of the ROMS Forum.
This Git repository is the official version of the code which only the developers are allowed to change. Users should download the ROMS code to their local machines using a git client. Don't attempt to use a regular web browser to browse or download files from the Git repository - there are much better tools for interacting with the code repository. See the notes below under the heading View the Repository.
We strongly recommend users always check out the current master version since this has the most recent updates and bug fixes. The tags are kept largely as a historical record of stable releases at the conclusion of major code upgrades.
If you are making changes of your own, keep them in a separate branch, leaving the master branch to track changes from the source. Git makes it so much easier to manage your own modifications than svn for those of us without write permission on the repository.
Below is a general description of how Git works. Please look at the Pro Git book for more detailed information. We have not yet tried any GUI clients but may add brief how-tos for the most popular GUIs at a later date.
Saving ROMS Login Credentials
To avoid having to type your ROMS password many times while executing the steps in the Downloading ROMS section below, we suggest you setup a git credential manager.
NOTE: If you have already setup a credential manager for other git repositories you should be able to add an entry for myroms following the documentation for the credential manager you are using.
There are a few different options for storing your ROMS login credentials in order to avoid having to type your username and password for every command. See here for more details. The simplest way to save your credentials is to use the built-in git-credential-store option. This option is very similar to the default way older Subversion clients store credentials so keep in mind that both your username and password will be stored without encryption in plain text. To use this method, execute the following:
This will create a plain text file that only the file owner (you) has permission to access.
Saving Login Credentials Securely on Mac OS
If you are working on Mac OS there is a simple option for securely storing you credentials using the OS X Keychain. Simply execute:
A window may pop up asking for your system's password to allow the credentials to be stored in your Keychain.
Saving Login Credentials Securely on Linux
Saving your credentials securely on Linux is a bit more complex and requires extra utilities (GPG) and configuration. This processes is adapted from here and requires Git version 1.8.3 or higher and GNU Privacy Guard (GnuPG or GPG). If you already use GPG and have a trusted key already you can skip the first step.
- Create a GPG key:> gpg --gen-key
gpg (GnuPG) 2.0.22; Copyright (C) 2013 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Please select what kind of key you want:
(1) RSA and RSA (default)
(2) DSA and Elgamal
(3) DSA (sign only)
(4) RSA (sign only)
Your selection? 1
RSA keys may be between 1024 and 4096 bits long.
What keysize do you want? (2048) 4096
Requested keysize is 4096 bits
Please specify how long the key should be valid.
0 = key does not expire
<n> = key expires in n days
<n>w = key expires in n weeks
<n>m = key expires in n months
<n>y = key expires in n years
Key is valid for? (0) 0
Key does not expire at all
Is this correct? (y/N) y
GnuPG needs to construct a user ID to identify your key.
Real name: Joe Roms
Email address: joe_roms@host.com
Comment: GPG Key
You selected this USER-ID:
'David Robertson <robertson@marine.rutgers.edu>'
Change (N)ame, (C)omment, (E)mail or (O)kay/(Q)uit? O
You need a Passphrase to protect your secret key.
# You will be asked to type your passphrase twice
We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform
some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the
disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number
generator a better chance to gain enough entropy.
gpg: key 33EA0E26 marked as ultimately trusted
public and secret key created and signed.
gpg: checking the trustdb
gpg: 3 marginal(s) needed, 1 complete(s) needed, classic trust model
gpg: depth: 0 valid: 2 signed: 0 trust: 0-, 0q, 0n, 0m, 0f, 2u
pub 4096R/33EA0E26 2019-06-05
Key fingerprint = 2CA2 904C A7DE CAEF 2266 70F6 1C74 375B 33EA 0E26
uid Joe Roms <joe_roms@host.com>
sub 4096R/5A0EDB59 2019-06-05
- Download the git-credential-netrc helper script from github and install it in a directory within your PATH. If there a multiple Git users on your system, you might want to have a system administrator place the script in /usr/bin or /usr/local/bin so all users will have access to it:> curl -o ~/bin/git-credential-netrc https://raw.githubusercontent.com/git/git/master/contrib/credential/netrc/git-credential-netrc
- Make a .netrc file in your home directory in clear text using your favorite text editor:Enter the following text (replacing joe_roms and secret with your ROMS username and password) and save the file:machine www.myroms.orgYou can add other blocks like the one above for other servers as well.
login joe_roms
password secret
protocol https
- Encrypt that file:This will create a file named .netrc.gpg. You can now safely delete the .netrc file (the unecrypted one).
- Use the newly encrypted file for all git operations that require credentials:> git config --global credential.helper 'netrc -f ~/.netrc.gpg -v'or for just a specific respoitory:> cd /path/to/repositoryThe first option will save the configuration to ~/.gitconfig while the second option will save to .git/config for the current git repository.
> git config --local credential.helper 'netrc -f ~/.netrc.gpg -v'
From now on, any Git command using an HTTPS URL which requires authentication will decrypt that .netrc.gpg file and use the login/password associated to the server you are contacting. The first time, GPG will ask you for the passphrase of your GPG key, to decrypt the file. The other times, the gpg-agent launched automatically by the first GPG call will provide that passphrase for you.
Note: If your system's gpg program has a different name you will need to change the 'git config' line accordingly. For example, on an UBUNTU machine the command would look something like this:
Saving Login Credentials Securely on Windows
We will add this once tested but you can follow the steps here if you would like to try it yourself.
Downloading ROMS
WARNING: It is strongly suggested that you clone the ROMS source code using the same operating system you wish to compile and run ROMS on. If you download the code on a Windows machine and wish to run it on a non-Windows machine you will need convert the line endings with a utility like dos2unix or recode. Even with these utilities you may still have problems compiling ROMS.
NOTE: To avoid having to type your ROMS password many times while executing the steps below, we suggest you first set up a git credential manager as described in the Saving ROMS Login Credentials section above. If you have already setup a credential manager for other git repositories you should be able to add an entry for myroms following the documentation for the credential manager you are using.
In order download source code from a git repository, git client software must be installed on your local machine. Most Linux distributions come with git, so shell commands may be used without installing additional software. The general form of git commands is:
To check-out the files from the ROMS repository master (latest version), enter (notice https instead of http):
where MyDir is the destination directory on your local computer. It will be created if not found. If your want to avoid typing your username for all future code updates, change the command to:
You only clone once because Git will keep track of the source, destination and a bunch of other information. For more detail on command line use and syntax, see the Pro Git book.
In order to synchronize the Git and Subversion repository revision information, we have created a Git filter that will insert the git hash of the last time a file was modified, similar to the Subversion $Id$ keyword. In order for the filter to work, it has to be explicitly enabled by the user. After the git clone command from above completes change into MyDir and execute the following:
In order to get the Git Id hashes to fill in, you will need to force the smudge filter to run on the source code you have already downloaded. This takes several minutes but only needs to be done once. For bash shells execute:
For csh/tcsh shells execute:
If you look at the top of any ROMS source file downloaded from the git repository, you will see both the Git commit hash for the last time that file was modified and the corresponding SVN revision properties. For example, the first few lines of ROMS/Modules/mod_ncparam.F look like this:MODULE mod_ncparam
!
!git $Id: b42658ab652647fca27d50af4afa15c3401fe544 $
!svn $Id: mod_ncparam.F 968 2019-06-17 16:02:48Z arango $
! Hernan G. Arango
! Copyright (c) 2002-2019 The ROMS/TOMS Group !
! Licensed under a MIT/X style license !
! See License_ROMS.txt !
!
While you are getting your configuration in order, you also want to tell git who you are:
This is important if you plan to ever commit your own modifications.
Several GUI front-ends to Git exist, allowing the user to have visual prompts to help them manage their files and credentials.
Updates
Now and again, you might feel the urge to get up to speed with the latest changes that have been made to the ROMS repository. When that happens, simply go to the directory that was 'MyDir' above and type:
Git will remember where you checked out from before and see if a newer revision exists. If so, it will download and apply all the relevant changes.

Using GUI Git Clients
WARNING: It is strongly suggested that you checkout the ROMS source code using the same operating system you wish to compile and run ROMS on. If you download the code on a Windows machine and wish to run it on a non-Windows machine you will need convert the line endings with a utility like dos2unix or recode. Even with these utilities you may still have problems compiling ROMS.
Once we have some experience with some GUI Git clients, we will add to this section.
View the Repository
The easiest way to view a repository is to simply look at it with Trac in a web browser. Enter the URL:
and log in with your ROMS credentials. Once logged in, click the Browse Source tab near the top of the page. This is also a good way to see individual files in the repository without actually downloading them.
Managing Your Own Modifications
This assumes that you have a fresh clone of the myroms repository on the master branch. You want to keep master as a pure copy of the source version and keep your own changes in say the arctic branch. Start by creating a branch and switching to it:
Now you can make whatever modifications you like (and test them out). To see what changed, you can use git status and git diff. To save your changes, do a:
Though if you add new files you will have to git add them first.
Getting the Updates
It is easy to fetch and merge the updates. Start by making sure your directory has been cleanly checked in with git status. Then you can update your master branch:
Then bring the changes into your arctic branch:
This will bring in everything that changed since your last git pull, so you might find it easier to keep on top of things by doing this often, not putting it off for years. You can also bring in changes one at a time with git cherry-pick. Again, check the Pro Git book for much more information about all of these operations.
Note that this will save your arctic branch locally, under the .git directory. You can back this up as you would any other important files you have. The gitish way to back it up is to the cloud, say on github. In the best of all possible open source projects, the master would be on github too, and you'd simply fork from it there. If you want to try this out, fork from Mark Hadfield's copy of the myroms source at [1].
8min Read
Almost every development and software projects, commercial or personal, are now using Git for version control. In this article, we will explain what Git is at a glance and recommend the best Git GUI clients for various platforms.
- Git Clients for Linux
- Git Clients for Windows
- Git Clients for Mac
- Cross-platform Git Clients
What Is Git?
Git is a popular open-source version control system among developers. Originally, it was designed for collaborative projects between developers. Git is mostly used to store content and code in repositories.
The system also provides an environment where the code can be changed, with the revisions saved for future use. The repositories are stored in a remote server but are locally saved in every team member’s computers.
Git can be accessed and managed using command line tools. But if you’re new to Git, then you might want to start with something more manageable.
Graphical User Interface (GUI) clients are tools that provide alternative visualization for Git.
Check our in-depth explanation on Git if you need more information. To know about the best Git GUI clients for platforms such as Linux, Windows, and Mac, keep on scrolling.
Git Clients for Linux
Looking for Git GUI clients that work on Linux and choosing the one that is compatible for you can be time-consuming. To make it much easier, we’ve listed some for you:
1. QGit
QGit is a free Git GUI for Linux that can graphically show different branches and allows you to see patch content and changes in files. With this tool, you can view archive trees, file histories, revisions, and diffs.
You’re also able to compare files, and visually change modified content using QGit. Applying or formatting patch series from selected commits, and moving commits between two QGit instances are also possible.
You can use the same semantic of Git commits to create new patches and implement common StGit commands. Scripts and commands sequences can be connected to a custom action.
2. Gitg
The user interface of Gitg is straightforward to use. It can open existing Git repositories saved in your computer. You can download the software for free, and it has a GPLv2 license. Remote repositories can also be viewed using Gitg.
Gitg enables you to perform common Git operations, browse commits, and preview files. You can see commit messages, untracked and unstaged commits through the commit view.
The downside of this tool is that large files tend to load slower, and it doesn’t show a project’s history.
3. Git Force
Git Force is a visual front-end tool for Git that runs on Linux as well as Windows, and it’s free to download. This software will help beginners as the interface is intuitive with a drag and drop feature, and it can be used solely without calling a command line Git tool.
You can create multiple Git repositories and branches, managing them all using Git Force. The tool is able to support one or more remote repositories and can quickly scan local ones.
The work you do in a git repository will be picked up by Git Force on the first refresh. However, it only works on most common Git commands, and because of that, it doesn’t keep any detailed state information.
Git Clients for Windows
There are also Git GUI clients that work well on Windows platforms. We’ve picked the top ones for you:
1. Sourcetree
Sourcetree is a free Git GUI client and can work on both Windows or Mac. This tool is simple to use yet powerful, making it perfect for both beginners and advanced users. The clean and elegant interface makes it effortless and enjoyable to navigate through.
It’s a fully featured GUI that makes your Git projects efficient and easier. It can support large Git files and visualize it with detailed branching diagrams, making it easy for you and your team members to see the progress.
The local commit search allows you to find file changes, commits, and branches while the remote repo manager lets you search and clone remote repositories within Sourcetree. You can also get clear and clean commits with the interactive rebase tool.
2. GitHub
If your remote repository is at GitHub, then this tool will be the most useful for you. The software is basically an extension of your work-flow in GitHub. By simply login in using your GitHub account, you can start working on your repositories.
GitHub Desktop is a free and open source Git GUI client. It has an intuitive interface that allows you to manage code without you needing to type commands. You can make new or add local repositories and perform Git operations with ease.
Creating branches and switching to existing ones isn’t a hassle, so is merging code with the master branch. Furthermore, you can track your changes with GitHub Desktop.
3. Tortoise Git
This open source and free software is a Windows shell interface for Git. It can be used in a commercial environment and be developed to your own version as well. Tortoise Git can be used with other development tools and any type of files.
It supports regular tasks like commit, creating branches and tags, showing logs, and so on. The tool is straightforward to use as commands are accessible straight from Windows Explorer. The dialogs are descriptive, and you’re able to move files by dragging them.
There are tools such as TortoiseGitMerge that help resolve conflicts and lets you see the changes you made to your files. It has a spell checker to log messages and auto-completion for keywords and paths. It’s also available in 30 different languages.
Git Clients for Mac
For Mac users, no need to worry as there are developers who’ve created Git GUI clients that run on Mac. A few of the recommended ones are:
1. GitUp
GitUp is a Git GUI client specifically for Mac users. It’s free to download, open source, and comes with GitUpKit – a toolkit that lets you build Git apps. The tool is easy to use and allows you to see your branches and merges clearly.
If you’re new to Git, GitUp offers a safe environment for you to learn and experiment. The interface is clutter-free, and it has a Live Map feature that lets you see your project’s progress without refreshing. Plus the Undo and Snapshot features enable you to change and record your steps.
Speed is one of the best things when it comes to GitUp. Not only it can load 40,000 commits in less than a second, but you can also instantly search for commits, branches, and tags in the repository. Git operations can’t get any quicker either since the tool is fully featured.
2. GitBox
This GIt GUI client has claimed that working with Git commands and operations can be easy as checking your mail. Well, it’s true since the tool allows you to commit, pull, and push code changes with one click.
With GitBox, you can automatically retrieve new commit from your server, avoiding merge commits and conflicts. You can also search for commits in the repository history by author or description.
Adding and undoing commands such as branch reset, cherry picking, and rebase is pretty straightforward as well when using GitBox.
You can download the software for free, and it’s also available on the Mac App Store with a license for $14.99. If you’re a student, you can get a 50% discount by scanning your student ID.
3. GitX-dev
GitX-dev is a free Git client for Mac, designed and created to be a first-class, maintainable tool for active developers. The tool is specialized for software developers, and it’s full-featured for most Git work-flows.
You can browse your repository history and view a nicely arranged diff of any revision. Plus you will also be able to see a complete tree of the revisions.
You can copy files by dragging them out of the tree and dropping them into your system or preview them with QuickLook.
Changes can be searched based on the author or subject. GitX-dev supports large repositories and all parameters of git-rev-list as well.
What Are The Best Git Clients For Macos Catalina
Cross-platform Git Clients
If you’re looking for Git clients that are all-rounders that can run in Linux, Windows, or Mac platforms, we’ve compiled a list below:
1. GitKraken
GitKraken is not only reliable, efficient, visually nice and stylish to use, but it also makes git operations understandable and enjoyable. Its interface is intuitive as it allows users to quickly perform basic actions, and has a drag and drop feature.
What is more, you can easily fix mistakes with one click.
The tool has a built-in code editor where you can start a new project and edit the files directly in GitKraken. Plus it lets you track your tasks as it can sync with GitHub in real time, organize tasks in the calendar view, and mention team members to notify them about updates.
The software is free for non-commercial use. But there are GitKraken Pro and Enterprise for business owners to use as well. Each cost $4.08/month and $8.25/month respectively.
2. SmartGit
Just like its name, this powerful Git GUI client has a smart interface that looks and works the same across different platforms.
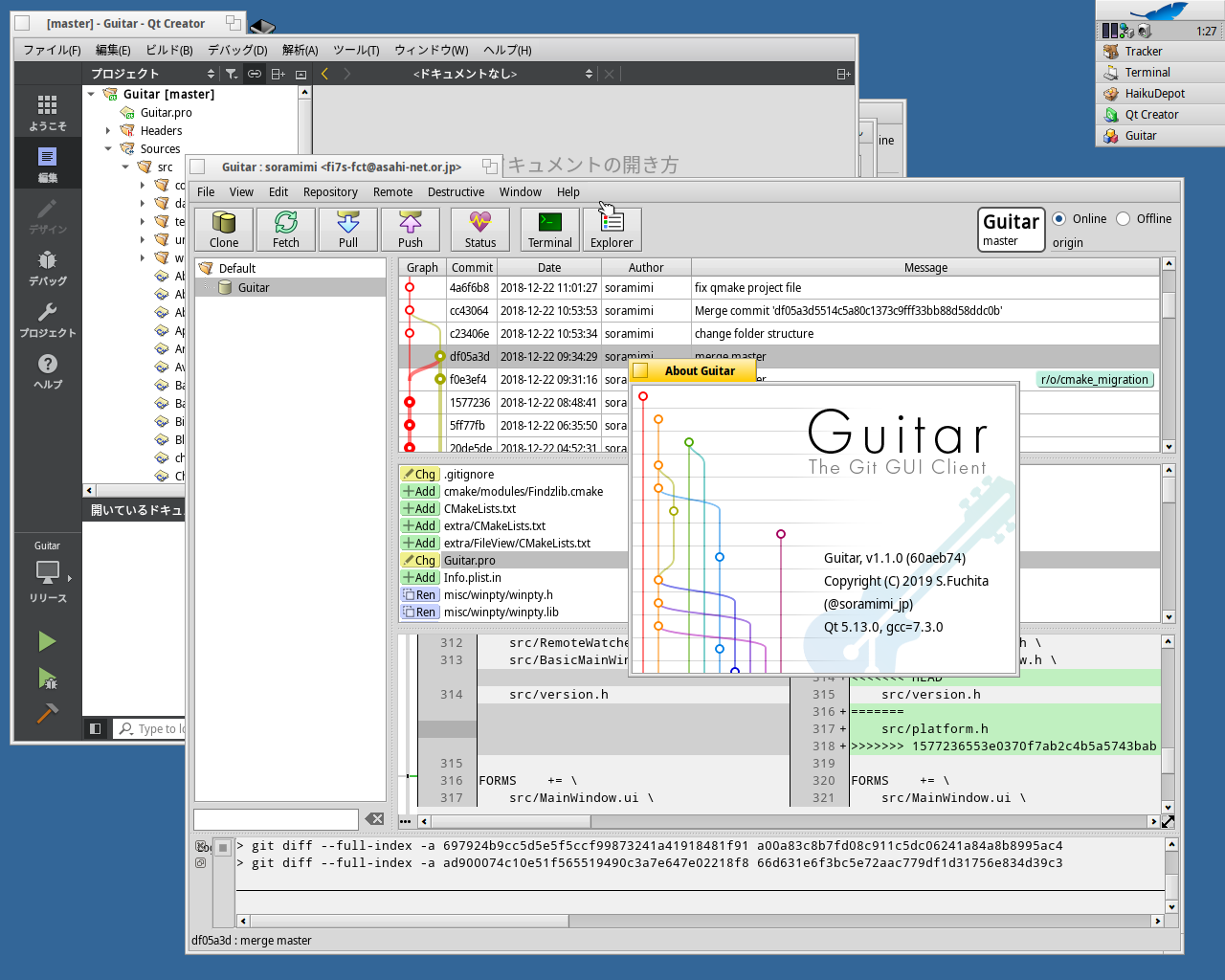
It has a single-view feature where you can see your index, working tree, and commands all in the Log window.
The tool lets you compare or merge files and edit them side-by-side. It can resolve merge conflicts by using the Conflict Solver. SmartGit also provides SSH client, an improved rebase performance and Git-Flow that allows you to configure branches without additional tools.
It integrates with popular Git platforms such as GitHub and BitBucket, making collaborative pull requests and code reviews easier.
The software is free to download. For commercial use, you can purchase a SmartGit license in a single payment ‒ $129 for a year to $319 for a lifetime or subscribe monthly for $8.99.
3. Git Cola
Git Cola is a simple yet powerful Git client that was developed using Python, and it’s free to use. The interface is made of multiple tools that you can hide and rearrange to your needs. The four panes of the interface allow you to view separate aspects of your project.
It also has Git-Dag, a Dag visualizer for commits and branches and the list of keyboard shortcuts is useful for an efficient and quicker work-flow.
Moreover, Git Cola will remember your work layout and restore it back to how it was the next time it’s launched.
Other than supporting custom GUI settings, the tool has language settings as well. Since Git Cola is open source, the tool is easy to maintain and update.
4. Aurees
Aurees is a multi-platform Git client that is simple and fast to use, plus free to download. Its interface is intuitive and clean. The tool aims to provide a smooth environment for users to view, edit, and publish Git files.
You need to log in to your GitHub account to use it.
Aurees shows commit and merging changes in side by side windows, making it effortless for you to trace back and resolve conflicts quickly. Tags are color coded so that you can navigate through the repo with ease.
With Aurees you can get an idea of which team member make what changes as it allows you to explore all documents. You can also indent merge commits to see line numbers or differences when comparing documents.
Conclusion
Git has become a necessity when it comes to managing collaborative development projects. However, it also has a high learning curve. Therefore, to make it easier for newcomers, developers have created Git Graphical User Interface clients for various platforms.
Let’s look back at the list once more,
Linux Git Clients:
What Are The Best Git Clients For Macos High Sierra
- QGit ‒ hassle-free Git GUI for Linux and it doesn’t cost a dime.
- Gitg ‒ you can view your repositories and it allows you to do common Git operations.
- Git Force ‒ beginners in Git can make use of this tool as it has an intuitive interface and it’s free to download.
Windows Git Clients:
- Sourcetree ‒ great for newcomers and experts in Git. A powerful tool, yet free and simple.
- GitHub for Windows ‒ a Git GUI where you can work on your project, visualize and track the workflow of your GitHub repositories.
- Tortoise Git ‒ an open source and free Git GUI for Windows, straightforward to use and can be used with other development tools.

Mac Git Clients:
- GitUp ‒ a safe environment to learn Git and experiment with. It’s also free, fast and easy to use.
- GitBox ‒ free for non-profit use and makes working with Git as easy as checking the mail.
- Git-Xdev ‒ designed to be a top and maintainable Git GUI. It’s free and full-featured for most workflows.
Multi-Platform Git Clients:
- Git Kraken ‒ has a free version, reliable, makes Git understandable, and visually appealing.
- SmartGit ‒ the interface is smart looking indeed and easy to use, free to download for non-commercial use.
- Git Cola ‒ a free, simple yet powerful Git client that makes work-flows quick and efficient.
- Aurees ‒ an easy to use free Git GUI client that enables users to work on Git operations effortlessly.
Enjoy going through the list and have fun checking them out. Good luck in finding the right Git GUI client for your project!
